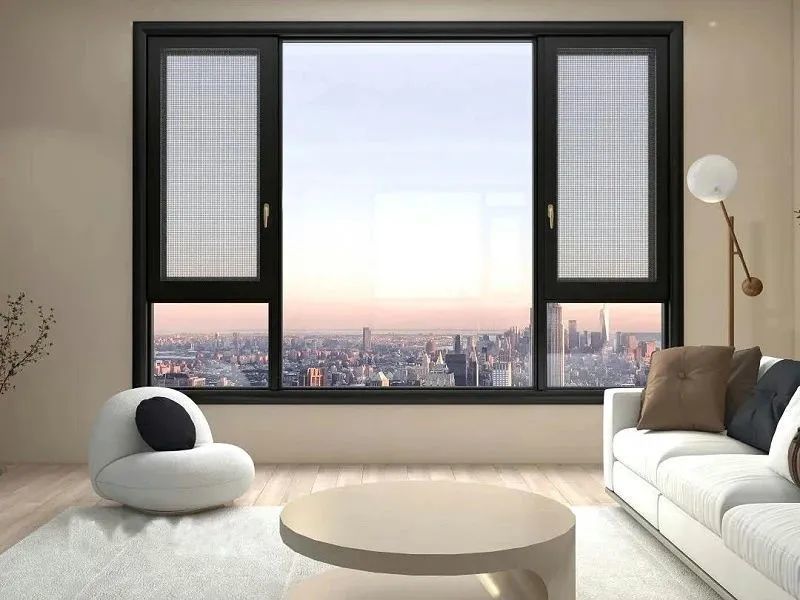
Casting properties of metals
Release time:
2023-12-28
sand casting
Sand casting has a wide range of adaptability, small pieces, large pieces, simple pieces, complex pieces, single pieces, large quantities can be used. Sand mold is more refractory than metal mold, so materials with higher melting points such as copper alloys and ferrous metals are also used in this process.
Sand casting mold, general wood production, commonly known as wood mold. In order to improve the dimensional accuracy is higher, but also often use a longer life of aluminum alloy mold or resin mold. Although the price has increased, it is still much cheaper than the mold used in metal casting, and the price advantage is particularly prominent in small batch and large production.
metal mold casting
When using metal mold casting, the following factors must be comprehensively considered: long manufacturing cycle, high cost, not suitable for single-piece and small-batch production; It is not suitable for casting complex shapes (especially inner cavities), thin-walled and large castings (metal molds are limited by the size of mold materials and the capacity of cavity processing equipment and casting equipment, so metal molds are not suitable for the production of particularly large castings).
gravity casting
It is widely used in the production of various non-ferrous castings, but metal mold casting also has the disadvantages of low metal utilization rate, difficult pouring of thin-walled complex castings, and low casting tissue density relative to pressure casting.
high pressure casting
Because the molten metal in the process of filling the cavity under high pressure and high speed, the air in the cavity will inevitably be clamped inside the casting to form subcutaneous pores, so aluminum alloy die castings should not be heat treated, and zinc alloy die castings should not be sprayed on the surface (but can be painted). Otherwise, the internal pores of the casting will be thermally expanded when heated as described above, resulting in deformation or bubbling of the casting.
The machining allowance of die castings should also be smaller, generally about 0.5mm, which can reduce the weight of the casting, reduce the amount of cutting to reduce the cost, and avoid penetrating the surface dense layer, exposing subcutaneous pores, causing the workpiece to be scrapped.
Due to the internal looseness of die-casting parts, poor plasticity and toughness, it is not suitable for manufacturing parts to withstand impact loads. The wall thickness of the casting is uniform, and it is advisable to use 3~4mm thin-walled castings, and the maximum wall thickness should be less than 6~8mm to prevent defects such as shrinkage cavity. Avoid machining to prevent internal holes from being exposed.
low pressure casting
Molten metal filling under pressure can improve the fluidity of molten metal, and the castings have good formability, which is conducive to the formation of castings with clear contours and smooth surfaces, and is more favorable for the formation of large thin-walled castings. The castings crystallize and solidify under pressure and can be fully replenished, so the castings have dense structure and high mechanical properties. The yield of molten metal is improved, in general, there is no need for risers, so that the yield of metal liquid is greatly improved, and the yield is generally up to 90%. Good working conditions, high production efficiency, easy to achieve mechanization and automation, but also the outstanding advantages of low pressure casting.
Low pressure casting has a wide range of applications for alloy grades and can basically be used for various casting alloys. Not only for casting non-ferrous alloys, but also for cast iron and cast steel. Especially for non-ferrous alloys that are easy to oxidize, it shows its superior performance, that is, it can effectively prevent the molten metal from oxidizing slag during the pouring process. Low pressure casting has no special requirements for mold materials.